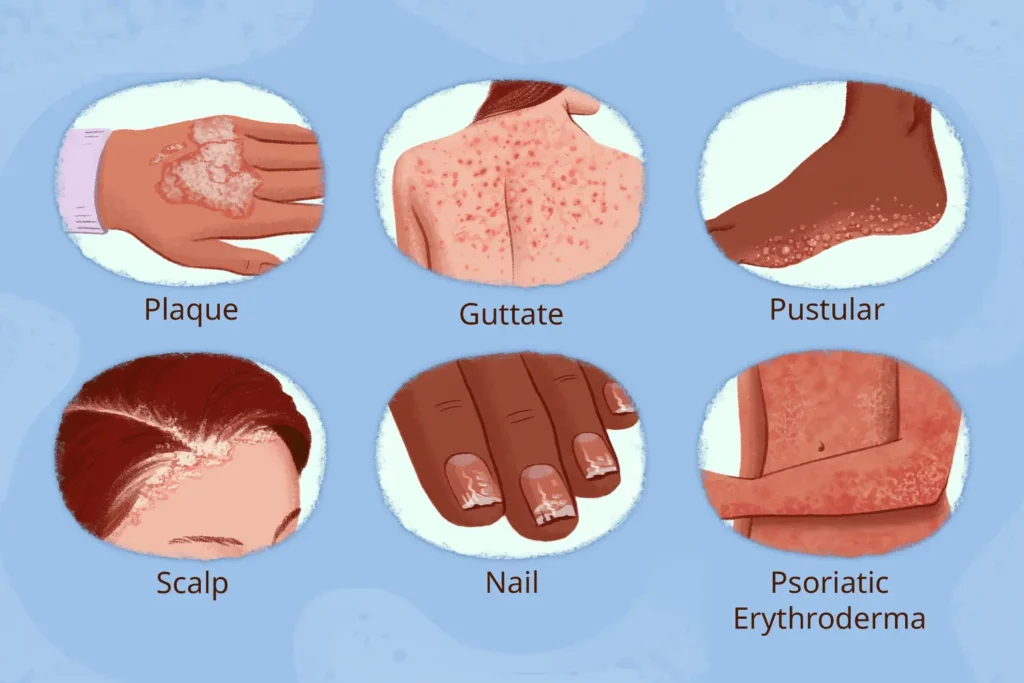
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the skin, causing rapid skin cell turnover, which leads to the development of scaly, red patches. These patches can be itchy, painful, and sometimes even debilitating. Psoriasis is not contagious, but it can be triggered by environmental factors, genetics, or immune system dysfunction. There are various types of psoriasis, each with its own set of symptoms and treatment options. In this article, we will explore the different types of psoriasis, their symptoms, causes, and the most effective treatment options available today.
What is Psoriasis?
Psoriasis is a chronic condition where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, speeding up the skin’s growth cycle. Normally, skin cells are replaced every 28 to 30 days, but in psoriasis, this process happens in just a few days. As a result, skin cells build up, forming thick, scaly patches. While the exact cause of psoriasis is not fully understood, it is believed to involve both genetic and environmental factors, including infections, stress, and cold weather.
If you’re struggling with skin health, you might also find useful tips in our article on skincare routine steps to help manage conditions like psoriasis and eczema.
Common Types of Psoriasis
1. Plaque Psoriasis
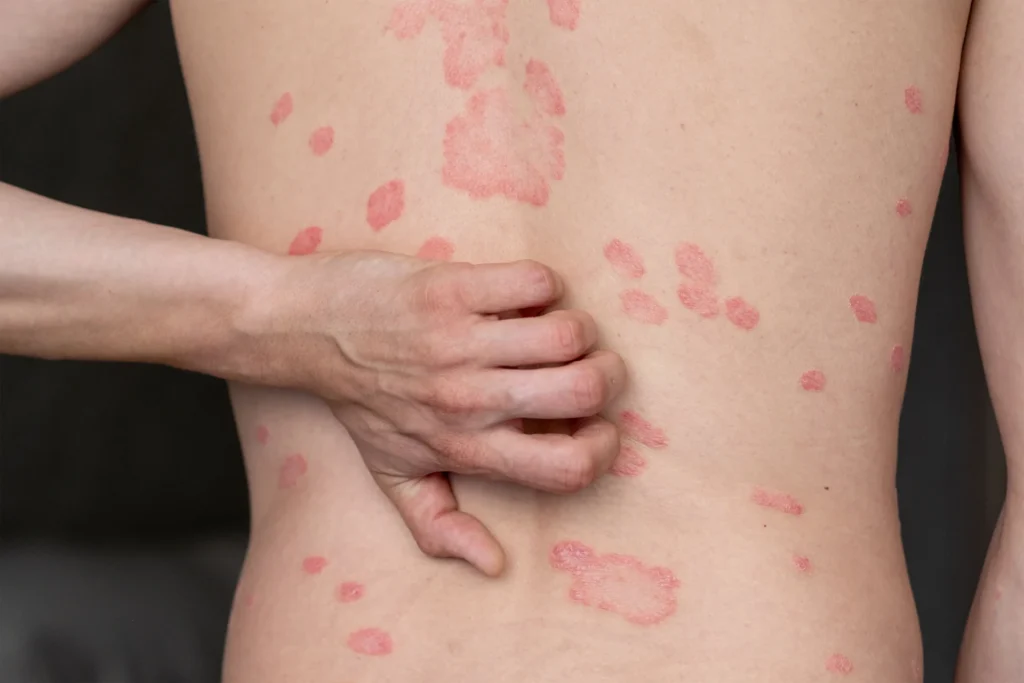
Plaque psoriasis is the most common form, affecting about 80% of people with psoriasis. This type is characterized by raised, red patches covered with silvery-white scales. These plaques are often found on the elbows, knees, and scalp. Plaque psoriasis photos and plaque psoriasis pictures can give a clearer visual of how these patches appear on the skin.
If you are specifically looking for treatments for the scalp, our article on dermoscopy for hair types may provide additional insights.
2. Scalp Psoriasis
Scalp psoriasis specifically affects the scalp, causing itching, flaking, and the formation of silvery scales. This type of psoriasis can extend beyond the hairline to the forehead, neck, or behind the ears. Scalp psoriasis treatment typically includes medicated shampoos and topical treatments to reduce inflammation and control flaking. If you’re looking for psoriasis on the scalp treatment, try options with coal tar or salicylic acid.
For more on maintaining healthy hair and scalp, visit our detailed guide on microneedling and its benefits.
3. Guttate Psoriasis
Guttate psoriasis appears as small, drop-like spots on the skin, often on the torso, arms, and legs. It is commonly triggered by infections such as strep throat. Although less common than plaque psoriasis, guttate psoriasis can be particularly challenging due to its sudden onset.
If you need more specific skin health advice, especially for managing common conditions, read our article on cucumber – the secret ingredient for skin.
4. Inverse Psoriasis
Inverse psoriasis affects the folds of the skin, such as the armpits, groin, or under the breasts. Unlike other types of psoriasis, the affected areas are typically smooth, red, and shiny. This form of psoriasis is particularly tricky because it is often mistaken for a fungal infection.
If you’re seeking solutions for other skin-related issues, check out our post on treatment of eczema on face.
5. Pustular Psoriasis
Pustular psoriasis causes white pustules or blisters surrounded by red skin. These pustules are typically localized, often found on the hands, feet, or fingertips. While pustular psoriasis can be a painful form of the disease, it can usually be managed with the right treatment.
For more about skin rejuvenation treatments, you may find our guide on hydrafacial before and after helpful.
6. Psoriasis Vulgaris
Psoriasis vulgaris is another term for plaque psoriasis. It is the most common form of psoriasis and involves the classic thick, red, scaly patches that can occur anywhere on the body.
Psoriasis Symptoms: How to Identify the Condition
The most common psoriasis symptoms include:
- Red, inflamed patches of skin
- Silvery-white scales on the skin
- Itching, burning, or soreness in the affected areas
- Dry, cracked skin that may bleed
- Thickened or ridged nails (known as nail psoriasis)
- Swollen or stiff joints (psoriatic arthritis)
If you notice these symptoms, it’s important to seek a diagnosis from a healthcare provider, as psoriasis can often be mistaken for eczema, a different skin condition. If you are dealing with skin inflammation or discomfort, consider reading more about related treatments, such as those discussed in our post on black pimples on face.
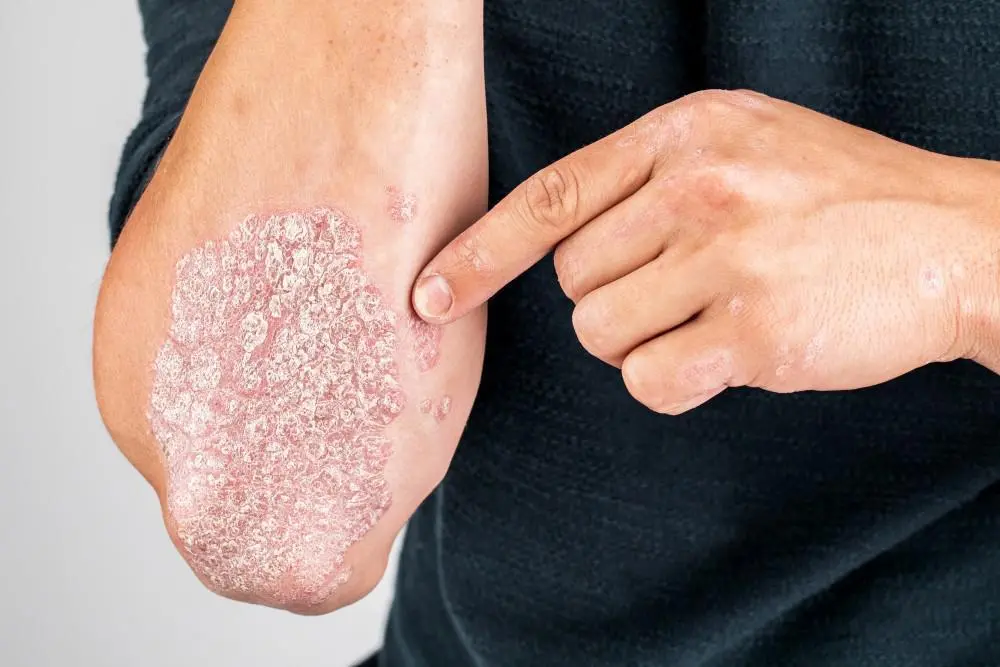
Psoriasis Causes: What Triggers Psoriasis?
While the exact cause of psoriasis is not fully known, there are several factors that are believed to trigger or worsen the condition:
- Genetics: A family history of psoriasis increases the likelihood of developing the disease.
- Immune System: Psoriasis is an autoimmune disorder, meaning the immune system attacks healthy skin cells.
- Environmental Factors: Stress, infections, cold weather, and certain medications can trigger flare-ups.
- Skin Injury: Cuts, scrapes, or sunburns can trigger a psoriasis flare-up, a phenomenon known as the Koebner response.
- Smoking and Alcohol: These lifestyle factors have been shown to increase the risk of developing psoriasis and worsen existing symptoms.
If you’re interested in the latest treatments for skin healing, visit our article on beef tallow for skin for more natural skincare options.
Psoriasis Treatment: How to Manage the Condition
While psoriasis is not curable, various treatments can help manage symptoms and reduce flare-ups. Treatment options vary depending on the severity and type of psoriasis:
1. Topical Treatments
- Topical corticosteroids: These are commonly used to reduce inflammation and relieve itching.
- Vitamin D analogs: These help slow down the production of skin cells.
- Coal tar: This can help reduce scaling and itching.
- Topical retinoids: Derived from vitamin A, these can help reduce skin cell growth. For mild psoriasis or localized patches, topical treatments are often the first line of defense.
2. Oral and Systemic Medications
For moderate to severe psoriasis, oral or systemic medications may be needed:
- Methotrexate: This can suppress the immune system and reduce skin cell turnover.
- Cyclosporine: Another immune-suppressing drug that helps manage severe psoriasis.
- Biologic drugs: These are newer medications that target specific parts of the immune system to reduce inflammation.
3. Light Therapy
Phototherapy, or light therapy, involves exposing the skin to ultraviolet (UV) light under medical supervision. This can slow the rapid skin cell turnover caused by psoriasis.
4. Psoriasis Shampoos
Medicated shampoos can help manage scalp psoriasis and reduce itching, flaking, and inflammation. Look for shampoos that contain ingredients like coal tar, salicylic acid, or ketoconazole. The best shampoo for psoriasis can often include these active ingredients to treat flaking, itching, and irritation.
You can also explore treatments for other skin conditions on our page about microneedling for acne scars.
Psoriasis vs. Eczema: What’s the Difference?
It’s common for people to confuse psoriasis with eczema due to their similar appearance, but they are different conditions. Psoriasis is an autoimmune disorder that speeds up skin cell turnover, while eczema is an inflammatory skin condition triggered by external factors like allergens or irritants. The main difference is that eczema often causes itching, while psoriasis is more likely to cause scaling and thickening of the skin.
Is Psoriasis Contagious?
No, psoriasis is not contagious. It cannot be spread from person to person through skin contact. However, it is important to note that psoriasis can be hereditary, and certain environmental factors can trigger flare-ups in those genetically predisposed to the condition.
How to Cure Psoriasis Permanently?
Currently, there is no cure for psoriasis, but there are many treatments available to manage the condition and control flare-ups. A combination of topical treatments, lifestyle changes, and in some cases, medications can help reduce symptoms and keep psoriasis under control for long periods.
Nail Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis
Nail psoriasis can affect both the nails and the surrounding skin. It causes pitting, thickening, and discoloration of the nails. In some cases, it can lead to complete nail loss. Similarly, psoriatic arthritis can occur alongside psoriasis, causing joint pain and swelling. Treatment for psoriatic arthritis often involves medications that target the immune system.
Conclusion: Living with Psoriasis
While psoriasis is a lifelong condition, effective treatments are available to manage symptoms and reduce flare-ups. Whether through topical treatments, medications, or light therapy, it’s important to find a psoriasis treatment plan that works for you. If you suspect you have psoriasis, consult a dermatologist to get an accurate diagnosis and explore the best treatment options for your case.
Disclaimer:
This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Please consult with a healthcare provider for personalized treatment and diagnosis of psoriasis.