Dermoscopy for hair types, also known as trichoscopy when applied to hair and scalp analysis, is a non-invasive diagnostic tool used to examine hair structures and scalp conditions under magnification. It provides valuable insights into the unique characteristics of different hair types, their health, and underlying scalp disorders.
This article delves into the dermoscopic examination of various hair types, highlighting its significance for dermatologists and trichologists in clinical and aesthetic practices.
Why Dermoscopy for Hair Types Matters?
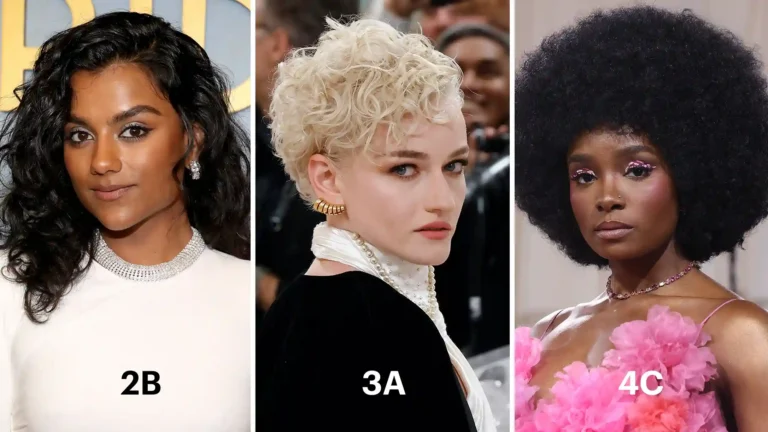
Understanding the dermoscopic features of different hair types and textures (1A to 4C) helps in:
- Diagnosing Scalp Disorders: Identifying issues like alopecia, seborrheic dermatitis, or tinea capitis.
- Assessing Hair Health: Detecting signs of breakage, thinning, or abnormalities in the hair shaft.
- Guiding Treatments: Tailoring medical or cosmetic interventions based on the specific needs of the hair type.
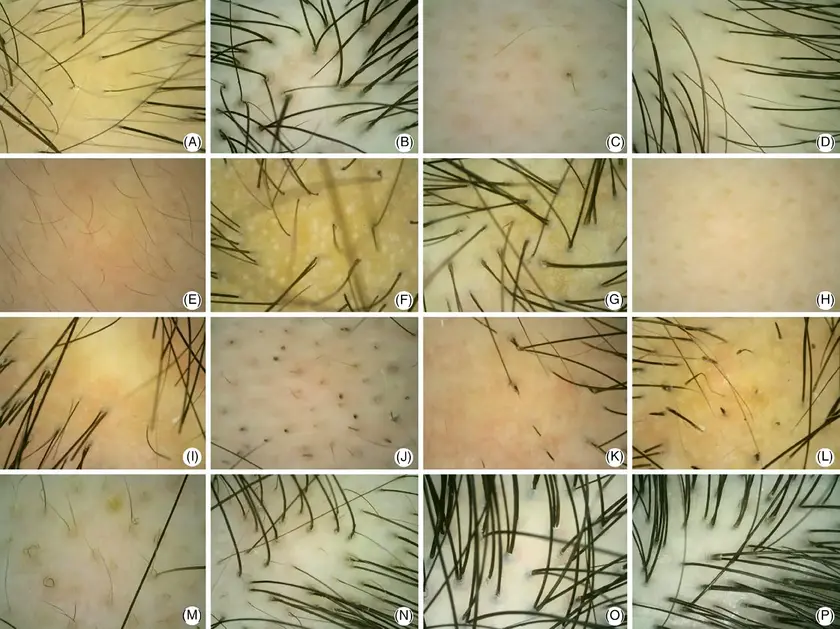
Dermoscopic Findings in Straight Hair (Type 1)
Key Characteristics:
Straight hair (Types 1A–1C) has a smooth, circular cuticle pattern, making it highly reflective.
- Follicular Openings: Uniform, round, and evenly distributed.
- Shaft Appearance: Cylindrical with minimal variation.
- Sebum Accumulation: Frequently visible, especially in 1A, due to the efficient distribution of scalp oils.
Common Conditions Diagnosed:
- Seborrheic Dermatitis: Visible as yellowish scales around the follicular openings.
- Telogen Effluvium: Increased short vellus hairs under dermoscopy.
Dermoscopic Features in Wavy Hair (Type 2)
Key Characteristics:
Wavy hair (Types 2A–2C) exhibits a gentle, S-shaped curve with a slight ellipticity of the hair shaft.
- Follicular Openings: May appear oval or slightly irregular due to the wave pattern.
- Shaft Appearance: Mild variations in diameter along the strand.
Common Conditions Diagnosed:
- Androgenetic Alopecia (AGA): Miniaturized hair follicles more apparent in wavy hair.
- Pityriasis Capitis (Dandruff): White, flaky scales visible around the scalp.
Dermoscopic Examination of Curly Hair (Type 3)
Key Characteristics:
Curly hair (Types 3A–3C) has a pronounced spiral or corkscrew structure.
- Follicular Openings: Irregularly shaped due to the twisting of the strands.
- Shaft Appearance: Variations in thickness and bends are visible under magnification.
Common Conditions Diagnosed:
- Traction Alopecia: Broken hairs at different lengths, especially near the hairline.
- Folliculitis: Red or yellow pustules around follicles are common due to improper care of curly textures.
- Related Article: Pain After Root Canal Treatment
Dermoscopic Findings in Coily/Kinky Hair (Type 4)
Key Characteristics:
Coily hair (Types 4A–4C) has a tightly coiled or zigzag pattern with high fragility.
- Follicular Openings: May appear clustered or spaced irregularly.
- Shaft Appearance: Thick but prone to micro-fractures.
- Perifollicular Hyperkeratosis: Common in coily textures due to reduced natural oil distribution.
Common Conditions Diagnosed:
- Scarring Alopecia: Early signs include perifollicular erythema and scaling.
- Pseudofolliculitis Barbae: Ingrown hairs, especially in tightly coiled strands.
Related Article: The Bold Hawk Nose
Common Dermoscopic Patterns Across Hair Types
| Pattern | Description | Associated Conditions |
|---|---|---|
| Yellow Dots | Sebaceous material in follicular openings | Alopecia Areata |
| Black Dots | Broken hair at the scalp level | Trichotillomania, Alopecia Areata |
| Exclamation Mark Hairs | Tapered hairs near the follicle | Alopecia Areata |
| White Scales | Scaling near follicles | Psoriasis, Seborrheic Dermatitis |
| Hair Shaft Fractures | Splitting or breaks in strands | Monilethrix, Traction Alopecia |
How Hair Texture Influences Dermoscopic Findings
The texture of hair affects its appearance under dermoscopy:
- Fine Hair: Easier to visualize follicular openings; common in Types 1A–1C.
- Thick Coarse Hair: More prone to shaft abnormalities such as twists or knots, often seen in Types 3C–4C.
- Porous Hair: Visible cracks or splitting, typically in chemically treated or damaged hair.
Clinical Applications of Dermoscopy in Hair Types
- Cosmetic Dermatology:
- Identifying damage from heat styling or chemical treatments.
- Tailoring products like moisturizing shampoos for curly or coily textures.
- Medical Diagnosis:
- Differentiating between scarring and non-scarring alopecia.
- Assessing the progression of conditions like lichen planopilaris or discoid lupus erythematosus.
- Treatment Monitoring:
- Evaluating response to treatments like minoxidil or platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy.
- Tracking hair regrowth patterns post-chemotherapy.
Dermoscopy Enhances Hair Care Across Types
Dermoscopy bridges the gap between aesthetic goals and clinical insights, allowing for precise diagnosis and effective treatment of hair and scalp issues. By understanding the unique dermoscopic features of different hair types, medical professionals can offer personalized care that promotes both health and beauty.
For expert consultations and advanced hair care treatments, visit The Face Clinic.







2 Comments
Comments are closed.