When it comes to skin concerns, pimples are a common and often frustrating issue that affects people of all ages. Among the different types of pimples, black pimples, commonly referred to as blackheads, are particularly troublesome due to their stubborn nature and visible appearance. Understanding what black pimples are, how they form, and how they differ from other types of acne is crucial for effective treatment and prevention.
What Are Black Pimples?
Black pimples, or blackheads, are a type of non-inflammatory acne that occurs when pores become clogged with a combination of dead skin cells, excess oil (sebum), and other impurities. Unlike whiteheads, which are closed at the surface and appear as small white bumps, blackheads have an open surface. This exposure to air causes the trapped material within the pore to oxidize, turning it dark or black in color. This process is what gives black pimples their characteristic appearance.
The formation of black pimples begins in the hair follicles, where sebaceous glands produce oil to lubricate and protect the skin. However, when these glands produce too much oil, it can mix with dead skin cells and other debris, forming a plug in the follicle. If the surface of this plug remains open, it oxidizes upon contact with air, leading to the formation of a blackhead.
Related Articles: Is Nocturnal Tooth Ache Neglectable?
Although black pimples are not typically painful like other forms of acne, such as cysts or pustules, they can be persistent and difficult to treat. They are most commonly found on areas of the face with a high concentration of oil glands, such as the nose, chin, and forehead, but they can also appear on the back, chest, and shoulders.
Why Understanding Different Types of Pimples Matters
Effective acne treatment starts with understanding the specific type of acne you’re dealing with. Black pimples, whiteheads, and cystic acne each have different causes, symptoms, and treatment methods. Misidentifying a type of pimple can lead to ineffective treatments that may exacerbate the problem.
- Black Pimples vs. Whiteheads: While black pimples and whiteheads both result from clogged pores, they differ in appearance and treatment. Whiteheads are closed at the surface, creating a white or flesh-colored bump, whereas black pimples have an open surface that turns black due to oxidation. Treatment for black pimples often focuses on keeping pores clear and preventing oxidation, whereas whiteheads may require different approaches, such as exfoliation to remove the surface layer of dead skin cells.
- Black Pimples vs. Cystic Acne: Cystic acne is a more severe form of acne that occurs when clogged pores become infected, leading to deep, painful cysts. Unlike black pimples, which are non-inflammatory and superficial, cystic acne involves deeper layers of the skin and requires more intensive treatment, often including prescription medications. Mistaking a cyst for a blackhead could lead to inadequate treatment and prolonged suffering.
- Why Accurate Identification Is Key: Accurately identifying the type of pimple is essential because it dictates the treatment approach. For instance, black pimples may respond well to over-the-counter treatments containing salicylic acid or benzoyl peroxide, which help to unclog pores and reduce oil production. On the other hand, cystic acne may require stronger, dermatologist-prescribed treatments like oral antibiotics or retinoids. Understanding these differences ensures that your skincare regimen is targeted and effective, minimizing the risk of scarring and further breakouts.
Related Article: A Guide to Different Nose Types
Understanding Acne and Cysts
Acne is a broad term that encompasses various types of skin blemishes, including blackheads, whiteheads, pustules, nodules, and cysts. Each type of acne lesion has its own characteristics and requires specific treatments. Among these, cystic acne is one of the most severe forms, often causing deep, painful lesions that can lead to permanent scarring if not treated properly. Understanding the differences between common acne and cystic acne, as well as the nuances of pimples that contain blood, is essential for managing and treating these conditions effectively.
Difference Between Acne and Cysts
Common Acne refers to the typical breakouts that many people experience, which include blackheads, whiteheads, and small pimples. These are usually caused by clogged pores resulting from excess oil production, dead skin cells, and bacteria. Common acne can range from mild to moderate, and while it can be frustrating, it is generally easier to treat with over-the-counter products and a consistent skincare routine.
- Blackheads: These are open comedones where the pore is clogged with oil and dead skin cells but remains open to the air. The exposure to air causes the material inside the pore to oxidize, turning it black.
- Whiteheads: These are closed comedones where the pore is clogged, but the surface of the pore remains closed. This results in a small, white or flesh-colored bump on the skin.
Cystic Acne, on the other hand, is a more severe form of acne that occurs when clogged pores become infected and inflamed. Unlike common acne, cystic acne lesions develop deeper within the skin, forming painful, pus-filled cysts that can be difficult to treat.
Related Article: Facial Fat Grafting: Rejuvenate Your Look Naturally
- Cysts vs Pimples on Face: Cysts are larger, deeper, and more painful than regular pimples. While a typical pimple may heal within a few days, cysts can last for weeks or even months. Cystic acne is often resistant to over-the-counter treatments and may require prescription medications such as oral antibiotics, retinoids, or hormonal treatments. The key difference between a cyst and a regular pimple is the depth of the inflammation and the potential for significant scarring if left untreated.
Understanding the difference between common acne and cystic acne is crucial because the treatment approaches are significantly different. Treating cystic acne as you would a simple pimple can lead to worsening inflammation and a higher risk of scarring.
Related Article: Everything You Need To Know About Aquiline Nose
What is a Cyst?
A cyst is a sac-like pocket of membranous tissue that can contain fluid, pus, or other materials. In the context of acne, a cyst forms when a pore becomes deeply infected and inflamed, creating a painful bump under the skin’s surface. Unlike other types of acne that remain near the surface of the skin, cystic acne occurs when the infection penetrates deeper into the skin, leading to more severe inflammation and damage.
- Cyst vs Pimple: The primary difference between a cyst and a pimple is the size, depth, and severity of the lesion. While a pimple may appear as a small, raised bump, a cyst is larger, often painful to the touch, and can feel like a hard lump under the skin. Cystic acne is more likely to cause scarring and requires different treatment strategies, often involving stronger medications or professional dermatological interventions.
Pimples with Blood and Blood-Filled Pimples
Pimples with Blood occur when the blood vessels under the skin are damaged due to inflammation or pressure, causing blood to mix with the pus inside the pimple. These types of pimples are often associated with more severe forms of acne, like cystic acne, where the inflammation is deeper and more extensive.
- Blood-Filled Pimples: These are a type of pimple that can appear particularly alarming due to the presence of blood. They occur when a pimple, especially a cystic one, is under significant pressure or has been picked at or squeezed, causing the underlying blood vessels to rupture. The blood then mixes with the pus, creating a red or purplish bump.
Blood-filled pimples are typically more painful and can take longer to heal than regular pimples. They also carry a higher risk of scarring, especially if they are popped or picked at. The presence of blood in a pimple is a sign of deeper inflammation, and such pimples should be treated carefully to avoid further complications.
Related Article: What Age Can You Get Rhinoplasty (Nose Job) In The UK?
What Causes Blood Pimples?
Blood pimples are often linked to more severe forms of acne, such as cystic acne, where the inflammation is deeper and more intense. Several factors can contribute to the formation of blood-filled pimples:
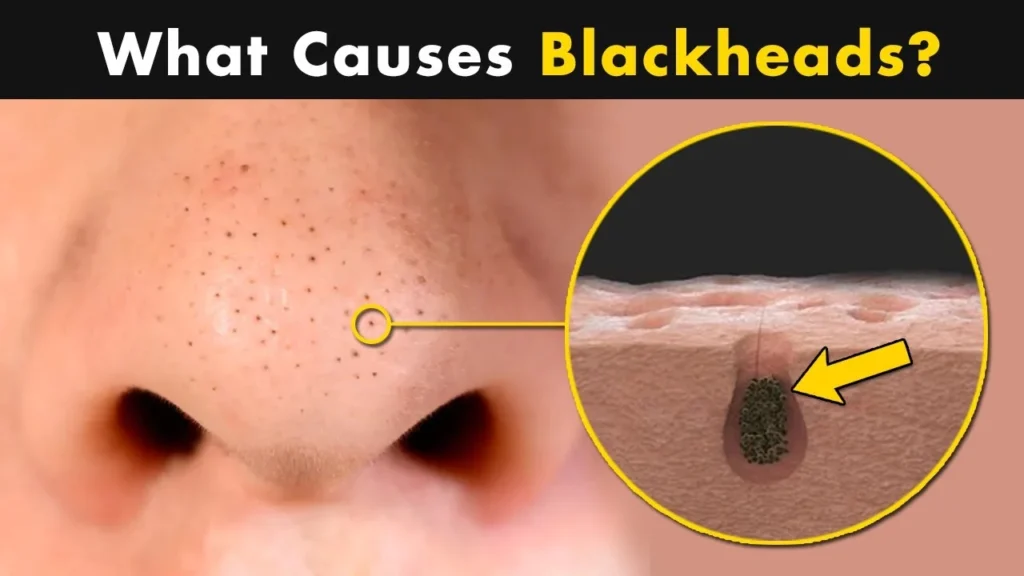
- Inflamed or Popped Cysts: One of the most common causes of blood pimples is an inflamed cyst. When a cyst becomes severely inflamed, the pressure within it can cause blood vessels to burst, leading to the formation of a blood-filled pimple. Popping or squeezing a cyst can also cause this outcome, as it can force the blood vessels to rupture.
- Excessive Picking or Squeezing: Attempting to pop or pick at pimples, particularly cystic ones, can cause the delicate blood vessels under the skin to break, leading to a blood-filled pimple. This is why dermatologists strongly advise against picking at pimples, as it can lead to more severe inflammation, infection, and scarring.
- Hormonal Fluctuations: Hormonal changes, especially during puberty, menstruation, or pregnancy, can exacerbate acne and lead to more severe forms of inflammation, increasing the likelihood of developing blood-filled pimples.
- Underlying Skin Conditions: Certain skin conditions or sensitivities can predispose individuals to develop more severe forms of acne, including blood-filled pimples. People with sensitive skin or those prone to conditions like rosacea may find that their acne is more likely to become inflamed and filled with blood.
Understanding the causes of blood pimples and their connection to cystic acne is important for both treatment and prevention. By recognizing the signs early and adopting appropriate skincare strategies, you can reduce the risk of developing these painful and potentially scarring lesions.
Related Article: Everything You Need to Know About Your Button Nose
Skincare for Acne and Dark Spots
Dealing with acne is challenging enough, but the aftermath often leaves lingering dark spots, medically known as post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH). These spots can be as distressing as the acne itself, particularly for individuals with darker skin tones, including those of Asian descent, where pigmentation issues are more pronounced. Addressing both acne and the dark spots that follow requires a targeted skincare approach, utilizing the right exfoliators, cleansers, and treatments like benzoyl peroxide. Below, we explore these solutions in detail, focusing on their effectiveness and suitability for different skin types.
Exfoliators for Dark Spots
Exfoliation is a critical step in managing dark spots left by acne. By removing the outer layer of dead skin cells, exfoliation helps to fade hyperpigmentation more quickly and allows for better absorption of other skincare products. However, it’s important to choose the right type of exfoliator based on your skin type, as over-exfoliation can lead to irritation and worsen dark spots.

- Chemical Exfoliators:
- Alpha Hydroxy Acids (AHAs): AHAs like glycolic acid and lactic acid are water-soluble acids that exfoliate the surface of the skin, making them ideal for fading dark spots. Glycolic acid, derived from sugar cane, is particularly effective due to its small molecular size, which allows it to penetrate the skin more deeply. AHAs are well-suited for individuals with normal to dry skin.
- Beta Hydroxy Acids (BHAs): Salicylic acid, a type of BHA, is oil-soluble, making it effective for acne-prone and oily skin. It exfoliates not only the surface but also deep within the pores, reducing the likelihood of future breakouts while addressing dark spots. Salicylic acid is also anti-inflammatory, making it suitable for sensitive skin prone to redness.
- Polyhydroxy Acids (PHAs): PHAs like gluconolactone are larger molecules that exfoliate more gently, making them ideal for sensitive skin types. They provide similar benefits to AHAs but with less irritation, which is crucial for people with darker skin tones, including those with Asian skin, who may be more prone to hyperpigmentation.
- Physical Exfoliators:
- While physical exfoliators like scrubs can be effective, they must be used with caution, especially on acne-prone or sensitive skin. Harsh scrubbing can lead to microtears in the skin, exacerbating acne and dark spots. If choosing a physical exfoliator, opt for one with fine, gentle particles and use it sparingly.
Exfoliation Tips:
- For Asian Skin: Due to the tendency of Asian skin to develop pigmentation issues, it’s advisable to start with a lower concentration of chemical exfoliators and gradually increase usage as the skin builds tolerance. Always follow exfoliation with sun protection, as freshly exfoliated skin is more susceptible to UV damage.
Related Article: Greek Nose: Everything you Need To Know
Acne and Dark Spot Cleansers
Choosing the right cleanser is essential for those battling both acne and dark spots. Cleansers formulated to address these concerns often contain ingredients that help to unclog pores, reduce inflammation, and fade hyperpigmentation.
- Salicylic Acid Cleansers:
- Salicylic Acid: This BHA is a common ingredient in acne cleansers due to its ability to penetrate and exfoliate within the pores, reducing the occurrence of acne. Additionally, its anti-inflammatory properties help to calm existing pimples and prevent post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. Using a salicylic acid cleanser can be particularly beneficial for those with oily or combination skin.
- Glycolic Acid Cleansers:
- Glycolic Acid: In cleansers, glycolic acid helps to gently exfoliate the skin’s surface, promoting cell turnover and fading dark spots. Regular use of glycolic acid cleansers can brighten the complexion and even out skin tone. It’s ideal for individuals with normal to dry skin.
- Niacinamide Cleansers:
- Niacinamide: This is a versatile ingredient that reduces inflammation, minimizes pore appearance, and lightens dark spots. Cleansers containing niacinamide are excellent for all skin types, including sensitive skin, as they provide gentle care while targeting multiple concerns.
- Vitamin C Cleansers:
- Vitamin C: Known for its brightening properties, vitamin C is an antioxidant that can help fade dark spots and protect the skin from environmental damage. Cleansers with vitamin C are effective in reducing pigmentation over time, but they should be used alongside broad-spectrum sunscreen during the day to prevent further darkening.
Related Article: Types of Noses in Females
Cleansing Tips:
- Consistency: Use these cleansers twice daily, morning and night, for best results. Avoid using multiple active ingredients simultaneously if you have sensitive skin to prevent irritation.
Benzoyl Peroxide for Scars and Dark Spots
Benzoyl Peroxide is a powerful acne-fighting ingredient known for its ability to kill acne-causing bacteria, reduce inflammation, and clear existing pimples. However, its role in treating scars and dark spots is more complex, as it can both help and hinder the healing process depending on how it’s used.
- How Benzoyl Peroxide Works:
- Benzoyl peroxide penetrates the skin to deliver oxygen into the pores, creating an environment that is inhospitable to the bacteria that cause acne. By reducing the number of acne-causing bacteria, benzoyl peroxide helps to clear existing breakouts and prevent new ones from forming.
- Benzoyl Peroxide and Scarring:
- Benzoyl Peroxide Scarring: While benzoyl peroxide is effective in treating active acne, it can potentially contribute to scarring if used incorrectly. High concentrations (above 2.5-5%) or overuse can lead to dryness, irritation, and increased inflammation, which may exacerbate post-acne scars. This is especially a concern for individuals with darker skin tones, who are more prone to developing hyperpigmentation and scarring.
- How to Use Benzoyl Peroxide Cautiously:
- Spot Treatment: Benzoyl peroxide is best used as a spot treatment rather than all-over application. Apply it directly to active pimples to reduce bacteria and inflammation without affecting the surrounding skin.
- Lower Concentrations: Start with a lower concentration (2.5%) to minimize the risk of irritation and potential scarring. Gradually increase the concentration only if needed and as your skin builds tolerance.
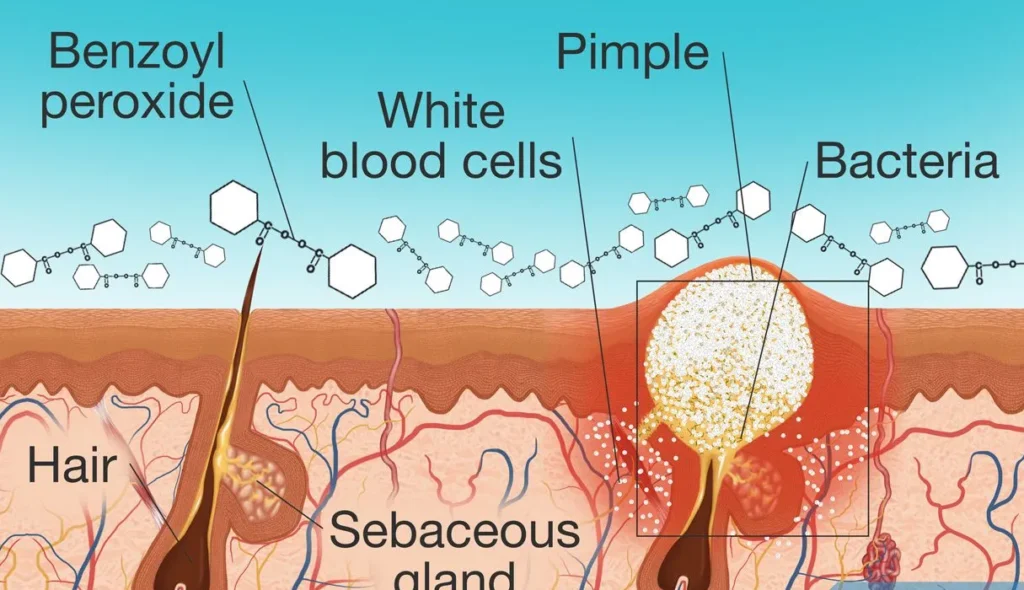
- Moisturization: Always follow benzoyl peroxide application with a hydrating moisturizer to combat dryness and maintain the skin’s barrier function.
- Avoiding Overuse: Overuse of benzoyl peroxide can lead to excessive dryness, which may prompt the skin to produce more oil, potentially worsening acne in the long term. Stick to recommended usage guidelines to prevent such outcomes.
Tips for Benzoyl Peroxide on Scars:
- For Dark Spots: While benzoyl peroxide is not typically used to treat dark spots directly, its role in preventing further breakouts is crucial in managing pigmentation issues. By controlling acne, you reduce the risk of developing new dark spots, allowing existing ones to fade over time with the help of other treatments like chemical exfoliants and brightening agents
Related Article: Treatment of Eczema on face
Specialized Treatments for Black Pimples
Black pimples, commonly known as blackheads, can be particularly stubborn and distressing. While they are not usually painful, their persistence and visibility can make them challenging to manage. Specialized treatments are available to address various aspects of blackheads and related issues, such as blood-filled pimples. This section will explore expert tips for treating blood-filled pimples, techniques for melting and dissolving blackheads, and the role of masks in targeting black spots on the face.
How to Get Rid of Blood-Filled Pimples
Blood-filled pimples are often an indication of deeper inflammation or trauma to the skin. They can be more painful and may require careful handling to avoid worsening the condition or leading to further scarring. Here are some expert tips for treating blood-filled pimples safely:
- Avoid Picking or Squeezing:
- Why It’s Important: Picking or squeezing blood-filled pimples can exacerbate the inflammation and lead to more severe scarring. It can also cause additional trauma to the blood vessels, making the issue worse.
- What to Do Instead: Apply a topical treatment directly to the pimple to reduce inflammation and promote healing.
- Use a Cold Compress:
- Application: Applying a cold compress can help reduce swelling and soothe the area. Use a clean cloth or ice pack wrapped in a thin towel to avoid direct contact with the skin.
- Duration: Apply the compress for 10-15 minutes several times a day to alleviate pain and reduce redness.
- Topical Treatments:
- Over-the-Counter Solutions: Look for products containing ingredients like benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, or sulfur. These ingredients can help to reduce inflammation and clear the pimple.
- Prescription Options: For severe cases, a dermatologist may prescribe topical antibiotics or corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and prevent infection.
- Seek Professional Help:
- When to See a Dermatologist: If blood-filled pimples persist, are recurrent, or show signs of infection, it’s essential to consult a dermatologist. Professional treatments like cortisone injections or laser therapy might be recommended for more severe cases.
- Avoid Irritating Products:
- What to Avoid: Harsh scrubs, astringents, and other irritating skincare products can worsen blood-filled pimples. Stick to gentle, non-comedogenic products that are formulated for sensitive skin.
Related Article: Hair Transplant Benefits and Negatives
Melting Blackheads and Dissolving Blackheads
Melting blackheads and dissolving blackheads refer to the use of specialized products that target the material inside pores, making it easier to clear out blackheads without physical extraction.
- Chemical Exfoliants:
- Salicylic Acid: Salicylic acid is a BHA that penetrates the pores, dissolving the debris that causes blackheads. It helps to exfoliate both the surface and inside the pores, making it easier for blackheads to be removed.
- Glycolic Acid: As an AHA, glycolic acid exfoliates the surface of the skin, improving overall skin texture and aiding in the removal of blackheads by promoting cell turnover.
- Clay Masks:
- Kaolin and Bentonite Clay: These clays absorb excess oil and impurities from the skin, helping to clear out blackheads. They work by drawing out the buildup from the pores, effectively “melting” away the blackheads.
- Application: Use clay masks once or twice a week to manage blackheads and maintain a clear complexion.
- Chemical Peels:
- Types: Chemical peels containing AHAs, BHAs, or a combination of both can help to dissolve blackheads by exfoliating the skin and breaking down the clog in the pores.
- Frequency: Peels should be used according to product instructions or under the guidance of a dermatologist to avoid over-exfoliation.
- Enzyme-Based Treatments:
- Ingredients: Products containing enzymes from fruits like papaya or pineapple can help dissolve dead skin cells and unclog pores. These are typically gentler than chemical exfoliants and can be suitable for sensitive skin.

Tips for Effective Use:
- Consistency: Regular use of these products is key to maintaining clear pores and preventing new blackheads from forming.
- Patch Testing: Always patch test new products to ensure they don’t cause irritation or allergic reactions.
Related Article: Best treatment options for old acne scars
Masks for Black Spots on Face
Masks can be a valuable addition to a skincare routine for treating black spots, also known as post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH). They work by targeting dark spots and improving overall skin tone. Here’s a review of effective masks and how to integrate them into your skincare regimen:
- Brightening Masks:
- Ingredients: Look for masks containing ingredients like vitamin C, niacinamide, and licorice extract. These ingredients are known for their brightening and pigmentation-reducing properties.
- Benefits: Brightening masks can help to even out skin tone and reduce the appearance of dark spots over time.
- Exfoliating Masks:
- Types: Masks with exfoliating acids (such as glycolic or lactic acid) can help to remove dead skin cells and promote the fading of dark spots by encouraging cell turnover.
- Usage: Use exfoliating masks once or twice a week to avoid over-exfoliation and irritation.
- Hydrating Masks:
- Ingredients: Masks with hyaluronic acid, aloe vera, or glycerin can help to hydrate the skin and improve its overall texture. While these masks may not directly target dark spots, they support a healthy skin barrier, making other treatments more effective.
- Benefits: Well-hydrated skin can better absorb brightening and exfoliating treatments, leading to improved results.
- Clay Masks with Added Ingredients:
- Combination: Clay masks that also contain brightening agents or exfoliants can be particularly effective for treating dark spots while also managing blackheads and excess oil.
- Application: Use these masks as directed, usually once a week, to balance the benefits of clay and active ingredients.
Integration into Routine:
- Frequency: Incorporate masks into your routine based on your skin type and needs. Typically, 1-2 times per week is sufficient for most masks.
- Combination Therapy: Combine masks with other treatments like chemical exfoliants and targeted serums for comprehensive management of dark spots and blackheads.
Addressing Specific Skin Concerns
When dealing with specific skin concerns, such as dark spots on Asian skin, pimples in stretch marks, and the role of hyaluronic acid in treating dark spots, it’s important to approach each issue with tailored strategies. Here’s a detailed exploration of these topics:
How to Get Rid of Dark Spots on Asian Skin
Dark spots, or post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH), can appear differently depending on skin tone. Asian skin, which often has a range of undertones and varying degrees of pigmentation, may require specific approaches for effective treatment.
- Understanding Dark Spots on Asian Skin:
- Hyperpigmentation: Asian skin can be prone to hyperpigmentation due to melanin production. Dark spots are often more prominent and can be harder to treat due to the increased melanin content.
- Sensitivity: Asian skin may be more sensitive to certain ingredients and treatments, necessitating a cautious approach.
- Effective Treatments:
- Vitamin C: Vitamin C is a potent antioxidant known for its brightening properties. It helps to inhibit melanin production and can lighten dark spots. Look for stable forms like ascorbic acid or ascorbyl glucoside.
- Niacinamide: This ingredient helps to reduce melanin transfer to skin cells, effectively lightening dark spots and improving skin texture. It’s also gentle and suitable for sensitive skin.
- Azelaic Acid: Azelaic acid addresses both acne and pigmentation. It works by inhibiting tyrosinase, an enzyme involved in melanin production, making it effective for treating dark spots.
- Licorice Extract: Known for its skin-brightening effects, licorice extract can help lighten dark spots and even out skin tone.
- Chemical Exfoliants: AHAs (like glycolic acid) and BHAs (like salicylic acid) can help in exfoliating dead skin cells, promoting cell turnover, and fading dark spots. They should be used carefully to avoid irritation.
- Sun Protection:
- Importance: Sun exposure can worsen dark spots and hinder the effectiveness of treatments. Using a broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher is crucial.
- Recommendation: Apply sunscreen daily, even on cloudy days, and reapply every 2 hours when exposed to sunlight.
- Professional Treatments:
- Laser Therapy: Laser treatments can target melanin and reduce the appearance of dark spots. Options like fractional laser and intense pulsed light (IPL) are commonly used.
- Chemical Peels: Professional chemical peels with stronger concentrations of AHAs or BHAs can accelerate the fading of dark spots.
Related Article: Top 10 Benefits of Face lift
Pimple in Stretch Marks
Pimples appearing in stretch marks can be an unusual but concerning issue. Stretch marks themselves are scars resulting from skin stretching, which can sometimes become prone to acne.
- Why Pimples Occur in Stretch Marks:
- Skin Changes: The skin’s structure changes with stretch marks, which can lead to clogged pores in these areas, resulting in acne.
- Increased Oil Production: The skin’s oil production can be uneven in areas with stretch marks, leading to breakouts.
- Treatment Strategies:
- Gentle Cleansing: Use a mild cleanser to keep the area clean and prevent further clogging of pores. Avoid harsh scrubs that can irritate the delicate skin around stretch marks.
- Topical Treatments: Apply treatments containing salicylic acid or benzoyl peroxide directly to the pimples. These ingredients help to reduce inflammation and unclog pores.
- Hydrating Products: Ensure the area is well-hydrated to maintain skin elasticity and reduce irritation. Use non-comedogenic moisturizers to prevent additional breakouts.
- Avoid Harsh Treatments: Be cautious with aggressive acne treatments that may cause further irritation or damage to the skin.
- Preventive Measures:
- Maintain Skin Elasticity: Keep the skin moisturized and use products that enhance skin elasticity to prevent the formation of new stretch marks and pimples.
- Monitor Changes: Regularly monitor the skin for any new changes or persistent issues, and consult a dermatologist if the condition worsens.
Hyaluronic Acid for Dark Spots
Hyaluronic Acid is primarily known for its hydrating properties, but its role in treating dark spots can be significant when used alongside other active ingredients.
- Role of Hyaluronic Acid:
- Hydration: Hyaluronic acid helps to maintain moisture in the skin, which is crucial for overall skin health and repair. Well-hydrated skin can better absorb other treatment ingredients.
- Skin Barrier Support: By strengthening the skin barrier, hyaluronic acid can help to reduce irritation and improve the effectiveness of other treatments for dark spots.
- Combination with Other Ingredients:
- Vitamin C: Combining hyaluronic acid with vitamin C enhances the brightening effect and supports skin hydration, creating a synergistic effect for treating dark spots.
- Niacinamide: Using hyaluronic acid with niacinamide can amplify the skin’s ability to lighten dark spots while keeping the skin hydrated and reducing inflammation.
- Retinoids: Incorporating hyaluronic acid with retinoids can improve the effectiveness of retinoids in fading dark spots while minimizing dryness and irritation.
- Application Tips:
- Layering: Apply hyaluronic acid after cleansing and before other treatment products. It should be used as a hydrating base that enhances the efficacy of other active ingredients.
- Frequency: Use hyaluronic acid twice daily, in the morning and evening, to maintain hydration and improve overall skin texture.
Long-Term Care and Prevention
Long-term care and prevention strategies are crucial for maintaining clear, healthy skin and managing persistent issues like cysts, pimples, and whiteheads. Understanding the differences in treatment approaches for cysts versus pimples, the timeline for whitehead healing, and the role of professional clinics can significantly enhance your skincare routine. Here’s a detailed guide on these aspects:
Cyst vs Pimple: Long-Term Skin Care
Cysts and pimples (including blackheads and whiteheads) require different long-term skincare strategies due to their varying nature and underlying causes.
- Cysts:
- What They Are: Cysts are deep, painful, and often inflamed lumps under the skin. They are filled with pus and can be more challenging to treat compared to superficial pimples.
- Treatment Approach:
- Medications: Prescription treatments such as oral antibiotics, retinoids, or corticosteroids may be necessary for severe cystic acne. These treatments help reduce inflammation and bacteria, preventing new cysts from forming.
- Topical Treatments: Benzoyl peroxide can be effective for reducing the bacteria that contribute to cysts, but it should be used cautiously to avoid excessive dryness and irritation. It’s often used in conjunction with other treatments prescribed by a dermatologist.
- Professional Care: Regular visits to a dermatologist for injections or drainage of cysts can help manage severe cases and prevent scarring.
- Long-Term Maintenance: Maintain a consistent skincare routine with gentle cleansers, non-comedogenic moisturizers, and sun protection. Avoid picking or squeezing cysts to reduce the risk of scarring.
- Pimples:
- What They Are: Pimples include various forms like blackheads, whiteheads, and papules. They are usually less severe than cysts but can still cause significant discomfort and blemishes.
- Treatment Approach:
- Over-the-Counter Solutions: Products containing salicylic acid, benzoyl peroxide, or alpha-hydroxy acids (AHAs) are effective for managing pimples. These ingredients help to unclog pores, reduce inflammation, and promote skin exfoliation.
- Preventive Measures: Regular exfoliation, using non-comedogenic products, and maintaining a balanced diet can help prevent new pimples from forming.
- Long-Term Maintenance: Incorporate a routine with gentle cleansers, targeted treatments, and sun protection. Adjust products based on skin changes and seasonal needs.
How Long for Whiteheads to Go Away?
Whiteheads, a type of non-inflammatory acne, can vary in healing time based on their severity and the treatment used. Here’s a general timeline and strategies to speed up the healing process:
- Typical Timeline:
- Mild Whiteheads: These can take 1-2 weeks to resolve with proper treatment. They usually clear up as the dead skin cells and sebum clogging the pore are removed.
- Moderate to Severe Whiteheads: These may take 2-4 weeks to improve, depending on the treatment and skin response.
- Speeding Up Healing:
- Topical Treatments: Use products containing salicylic acid or benzoyl peroxide to help dissolve the clog and reduce inflammation. These treatments can expedite the healing process.
- Exfoliation: Regular exfoliation with gentle products can help prevent the buildup of dead skin cells that contribute to whiteheads.
- Avoiding Irritation: Be cautious with harsh scrubs or astringents that can irritate the skin and worsen whiteheads. Stick to gentle, non-comedogenic products.
- Hydration: Keeping the skin well-hydrated can help support its healing process and prevent excessive dryness or irritation from treatments.
Acne Clinic San Leandro and Professional Treatments
For persistent or severe cases of black pimples and cystic acne, professional treatment from specialized clinics can provide significant benefits.
- Role of Acne Clinics:
- Expert Evaluation: Clinics offer thorough evaluations by dermatologists who can diagnose the severity of acne and recommend appropriate treatments.
- Advanced Treatments: Services such as chemical peels, laser therapy, and light-based treatments can target stubborn acne and improve overall skin appearance.
- Customized Plans: Clinics develop personalized treatment plans tailored to individual needs, combining prescription medications, professional procedures, and skincare routines.
- Benefits of Professional Care:
- Targeted Solutions: Professional treatments can address specific concerns more effectively than over-the-counter products, particularly for severe or resistant cases.
- Ongoing Support: Acne clinics provide ongoing support and adjustments to treatment plans based on skin response and progress.
- Prevention and Management: Professional guidance helps in preventing future breakouts and managing long-term skin health, ensuring a comprehensive approach to acne care.
- Choosing a Clinic:
- Reputation and Experience: Research clinics with a good reputation and experienced dermatologists. Consider reviews, success stories, and the range of treatments offered.
- Consultations: Schedule consultations to discuss your concerns, explore treatment options, and determine the best plan for your skin.
Understanding the differences between black pimples, acne, and cysts is essential for effective skincare. Each type of blemish requires a distinct approach for treatment and management. Here’s why it’s important to recognize these differences and choose the right treatment, as well as the value of seeking professional advice and being patient in your skincare journey





One Comment
Comments are closed.